
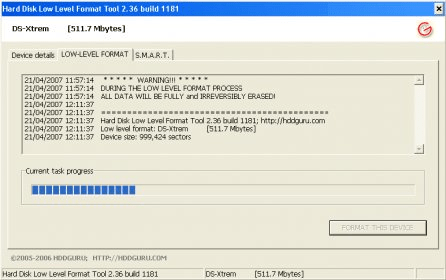
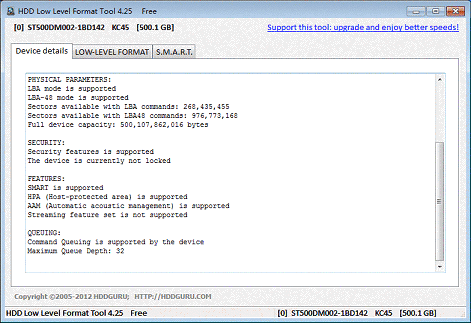
Disk and distributed file system may specify an optional boot block, and/or various volume and directory information for the operating system. This may occur during operating system installation, or when adding a new disk. This formatting includes the data structures used by the OS to identify the logical drive or partition's contents. High-level formatting creates the file system format within a disk partition or a logical volume.This level of formatting often includes checking for defective tracks or defective sectors. Partitioning divides a disk into one or more regions, writing data structures to the disk to indicate the beginning and end of the regions.This is intended to be the permanent foundation of the disk, and is often completed at the factory. Low-level formatting (i.e., closest to the hardware) marks the surfaces of the disks with markers indicating the start of a recording block (typically today called sector markers) and other information like block CRC to be used later, in normal operations, by the disk controller to read or write data.Optical discs generally only use fixed block sizes.įormatting a disk for use by an operating system and its applications typically involves three different processes. įloppy disks generally only used fixed block sizes but these sizes were a function of the host's OS and its interaction with its controller so that a particular type of media (e.g., 5¼-inch DSDD) would have different block sizes depending upon the host OS and controller.
BEST LOW LEVEL FORMAT TOOL SERIAL
Modern hard disk drives, such as Serial attached SCSI (SAS) and Serial ATA (SATA) drives, appear at their interfaces as a contiguous set of fixed-size blocks for many years 512 bytes long but beginning in 2009 and accelerating through 2011, all major hard disk drive manufacturers began releasing hard disk drive platforms using the Advanced Format of 4096 byte logical blocks. The disk subsystems and other Direct access storage devices on the IBM System/360 expanded this concept in the form of Count Key Data (CKD) and later Extended Count Key Data (ECKD) however the use of variable block size in HDDs fell out of use in the 1990s one of the last HDDs to support variable block size was the IBM 3390 Model 9, announced May 1993. the IBM 350 disk storage unit (of the late 1950s) block size was 100 six-bit characters) but starting with the 1301 IBM marketed subsystems that featured variable block sizes: a particular track could have blocks of different sizes. The earliest disk drives had fixed block sizes (e.g.
BEST LOW LEVEL FORMAT TOOL FREE
Special tools can remove user data by a single overwrite of all files and free space. Some formatting utilities allow distinguishing between a quick format, which does not erase all existing data and a long option that does erase all existing data.Īs a general rule, formatting a disk by default leaves most if not all existing data on the disk medium some or most of which might be recoverable with privileged or special tools. In some operating systems all or parts of these three processes can be combined or repeated at different levels and the term "format" is understood to mean an operation in which a new disk medium is fully prepared to store files. The third part of the process, usually termed "high-level formatting" most often refers to the process of generating a new file system. Partitioning is the common term for the second part of the process, dividing the device into several sub-devices and, in some cases, writing information to the device allowing an operating system to be booted from it. The first part of the formatting process that performs basic medium preparation is often referred to as "low-level formatting". In some cases, the formatting operation may also create one or more new file systems. Process of preparing a data storage device for initial useĭisk formatting is the process of preparing a data storage device such as a hard disk drive, solid-state drive, floppy disk or USB flash drive for initial use.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
